Chinese Medicine vs Western Medicine
| Chinese Medicine | Western Medicine | |
|---|---|---|
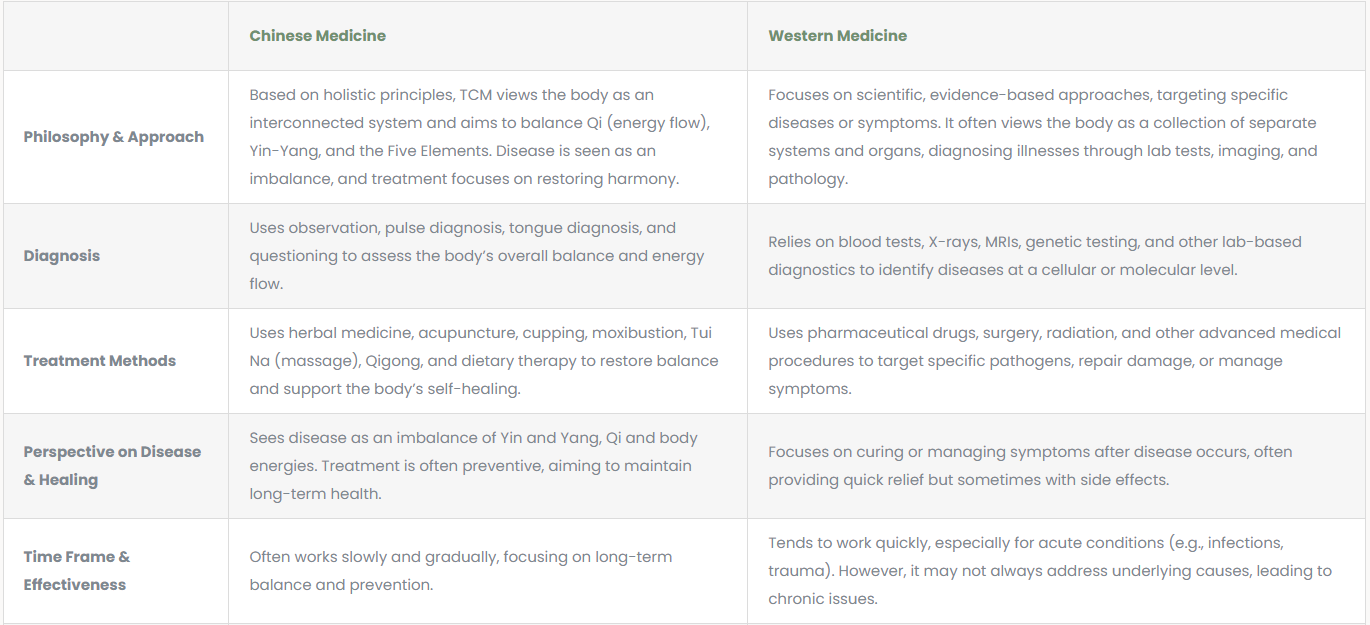
| Philosophy & Approach | Based on holistic principles, TCM views the body as an interconnected system and aims to balance Qi (energy flow), Yin-Yang, and the Five Elements. Disease is seen as an imbalance, and treatment focuses on restoring harmony. | Focuses on scientific, evidence-based approaches, targeting specific diseases or symptoms. It often views the body as a collection of separate systems and organs, diagnosing illnesses through lab tests, imaging, and pathology. |
| Diagnosis | Uses observation, pulse diagnosis, tongue diagnosis, and questioning to assess the body’s overall balance and energy flow. | Relies on blood tests, X-rays, MRIs, genetic testing, and other lab-based diagnostics to identify diseases at a cellular or molecular level. |
| Treatment Methods | Uses herbal medicine, acupuncture, cupping, moxibustion, Tui Na (massage), Qigong, and dietary therapy to restore balance and support the body’s self-healing. | Uses pharmaceutical drugs, surgery, radiation, and other advanced medical procedures to target specific pathogens, repair damage, or manage symptoms. |
| Perspective on Disease & Healing | Sees disease as an imbalance of Yin and Yang, Qi and body energies. Treatment is often preventive, aiming to maintain long-term health. | Focuses on curing or managing symptoms after disease occurs, often providing quick relief but sometimes with side effects. |
| Time Frame & Effectiveness | Often works slowly and gradually, focusing on long-term balance and prevention. | Tends to work quickly, especially for acute conditions (e.g., infections, trauma). However, it may not always address underlying causes, leading to chronic issues. |
| Pain Management |
Works well for chronic pain, offering a holistic, non-invasive approach with fewer side effects. |
Effective for acute pain but can lead to dependency (e.g., opioids). |
| Cancer Treatment |
Used as complementary care to reduce treatment side effects and improve quality of life. |
Directly attacks cancer but can weaken the immune system. |
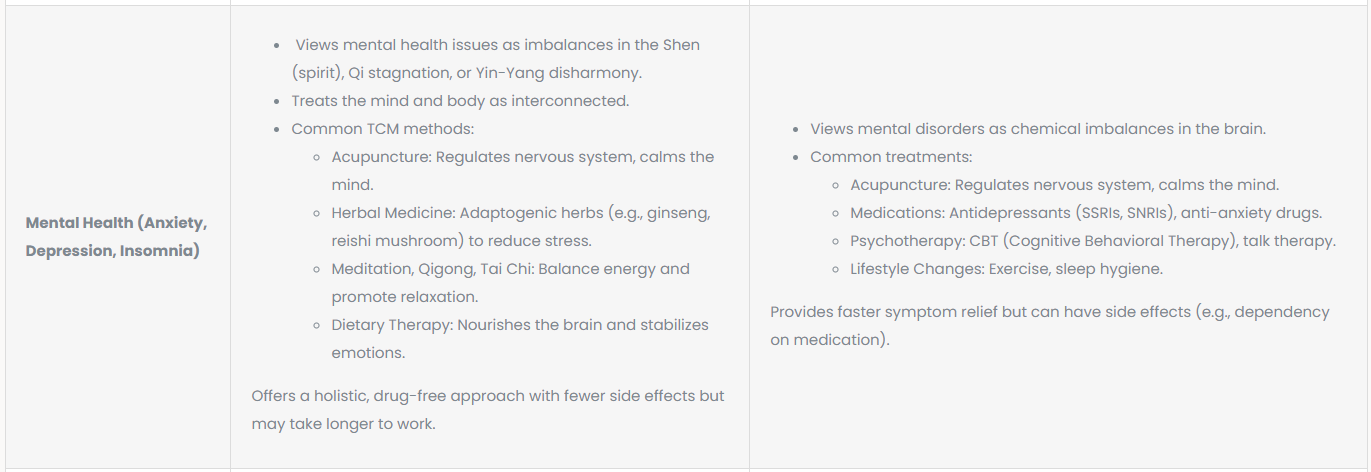
| Mental Health (Anxiety, Depression, Insomnia) |
Offers a holistic, drug-free approach with fewer side effects but may take longer to work. |
Provides faster symptom relief but can have side effects (e.g., dependency on medication). |
| Chronic Diseases (Diabetes, Hypertension, Autoimmune Disorders) |
Aims to treat the root cause and prevent disease progression. |
Controls symptoms effectively but may require lifelong medication. |
| Final Thoughts on Integration: Which One is Better? | valuable for chronic conditions, pain management, mental health, and long-term wellness.
Many people today use an integrative approach, combining Western medical diagnostics with TCM therapies for a balanced, holistic approach to health. |
best for acute, life-threatening conditions (e.g., infections, surgeries, cancer treatment).
In modern healthcare, there is increasing recognition of the complementary benefits of both systems. Some hospitals integrate acupuncture, herbal medicine, and dietary therapy alongside Western treatments for pain management, chronic disease, and mental health. |
We focus on the 5 Pillars of Health, in which acupuncture supports

At weMED Health, we are committed to
providing modern healthcare that bridges the
gap between Eastern and Western medicine.
At weMED Health, we are committed to providing modern healthcare that bridges the gap between Eastern and Western medicine.
Pain relief without
harmful medications
Avoid Expensive
Surgeries
Improve Your
Quality of Life














 Fill out the form below and we will get back with you shortly.
Fill out the form below and we will get back with you shortly. Fill out the form below and we will get back with you shortly.
Fill out the form below and we will get back with you shortly.